Class 12 Physics chapter 1 Electric charges and fields handwritten notes
- Electric charges: conservation of charge; Coulomb's law forces between two point charges; forces between multiple charges; the superposition principle; and continuous charge distribution
- Electric field: electric field due to a point charge, electric field lines, electric dipole, electric field due to a dipole, torque on a dipole in a uniform electric field
- Electric flux, Gauss's law, and its applications to find field are due to an infinitely long, uniformly charged straight wire, an infinitely charged plane sheet, and a uniformly charged thin spherical shell. Electric potential and its calculation for a point charge, an electric dipole, and a system of charges; Equipotential surfaces, the electrical potential energy of a system of two point charges in an electrostatic field
- Conductors and insulators, Dielectrics and electric polarization, capacitors, combinations of capacitors in series and in parallel, capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor with and without dielectric medium between the plates, energy stored in a capacitor
Chapter 1: Electric Charges and Fields
1. Electricity Fees
- Charge conservation
- Coulomb’s law of force between two point charges
- forces between multiple charges
- Superposition principle
- Continuous charge distribution
3. Electric flux, the statement of Gauss’s theorem, and its applications to finding field are due to an infinitely long straight wire, a uniformly charged infinite plane sheet, and a uniformly charged thin spherical shell (field inside and outside).
Download Timer
Electrostatics - study of forces, fields and potentials due to charges at rest.
Examples for static electricity are
- spark or hearing a crackle when we take off our synthetic clothes or sweater particularly in dry weather
- Sensation of an electric shock while opening the door of a car or holding the iron bar of a bus after sliding from our seat.
- Lightning
- A comb rubbed with hair attracts small pieces of paper etc.
Electric Charge
- Electric charge is the physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when placed in
- an electromagnetic field.
- The two types of charges are positive and negative (Named by Benjamin Franklin)
- Like charges repels and unlike charges attracts.
- When amber rubbed with wool or silk cloth attracts light objects – discovered by Thales.
- Electroscope – device for charge detection
- It is a scalar quantity .
- SI unit of electric charge- coulomb (C)
- Charge of a proton is positive (1.602192 × 10-19 C)
- Charge of an electron is negative (-1.602192 × 10-19 C)
- Matter with equal number of electrons and protons are electrically neutral.
- Matter with excess number of electrons – negatively charged
- Matter with excess protons – positively charged.
- Substances which allow passage of charges .
- Eg : Metals, human body etc
- The charge transferred to a conductor is distributed over the entire surface of the conductor.
- Substances which does not allow passage of charges.
- Eg: plastic, rubber etc.
- The charge transferred to an insulator stays at the same place.
- The process of sharing charges with earth.
- Earthing provides a safety measure for electrical circuits and appliances.
- When two bodies are rubbed electrons are transferred from material with lower work function to material with higher work function.
- Work function – energy required to remove an electron from a metal surface.
- Body gains electrons- negatively charged
- Body which loses electron – positively charged.
- Positively charged body – mass decreases
- Negatively charged body – mass increases
- When a charged body is brought in to contact with an uncharged conductor, charge flows from the charged body to the uncharged body.
- This is used to charge a conductor.
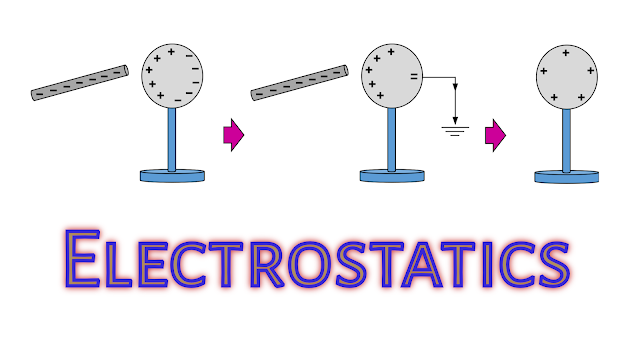
- When a charged body is brought near to an uncharged conductor (without touching), that end of the uncharged conductor which is near to the charged body gets oppositely charged and the farther end is charged with the same type of charge.
Class 12 Electric and Charges Fields Handwritten Notes PDF Download:
Students can download all chapter's notes by Chapterwise in Class 12 Physics, Chapter 1: Electric Charges and Fields. I have uploaded the handwritten notes for each chapter of charge and field for class 12 in a PDF file. I also collected handwritten notes for class XII for all subjects via the links provided in this article.
To get good grades in electric charges and electric fields, students must memorise the formulas. One way she does this is by poring over the class 12 notes on electric charges and electric fields. These formulas not only help students score well in school exams, but they also help in the CBSE Class 12 Electric Charges and Fields Board Exam.
Handwritten notebook PDF for 12th Physics Chapter 1 Electric charge and field
Preparing for the Class XII Board Exam is one of every student's top priorities. I also provided handwritten notes on charge and electric fields for the G12 preparation to help students solve this problem. All these 12th-grade handwritten notes on charges and fields (in PDF format) are written by experienced teachers who are well versed in charges and fields. By chapter, important handwritten notes for Grade 12 Charges and Fields are necessary for exam preparation and rapid repetition. The Electric Charges and Electric Fields study material contains the most weighted chapters, and their topics are specifically tested on the exam. The charge and electric field section syllabus for class 12 contains complex topics that are very difficult to master in a short time to prepare for the exam. To overcome this difficulty, I have devised handwritten notes on electric charges and electric fields so that I can concentrate only on the main topic of the chapter. Review all notes and download a handwritten note on Class 12 Charges and Electric Fields from the list below.
Meaning of Class 12 Charges and Handwritten Field Notes PDF
Review your handwritten notes for Class 12, Physics, Chapter 1, Electric Charges and Fields. 4-5 times a day to make sure you retain the maximum amount of information. We have compiled interactive examples and diagrams taken from previous year papers for the IIT JEE and other engineering exams, in addition to formulas and facts. Topics are added daily. You can also share suggestions in notes. You can also request handwritten notes on charge and field for specific topics in Class 12. Below are some of the benefits of these exclusive Class 12 Powerline Charge and Field Handwritten Notes.
Prepared by a seasoned and experienced faculty made up of former IITians. Based on the latest Class 12 syllabus and other engineering exams, covers almost all important facts and formulas.
They are presented in the clearest and most concise form.
Easy to notice.
Supported by illustrations from last year's paper.
The solution is detailed and easy to understand. These Class XII charge and field handwritten notes will help you prepare at the last minute.
These class 12 handwritten notes on charges and electric fields really help improve your score.
Chapter 12: Electric Charge and Electric Field Handwritten Notes PDF
Charges and Electric Fields Chapter for Class 12 Exam Preparation and Handwritten Notes for Quick Review These PDF Electric and Electric Field Notes are designed for students preparing for the JEE Main and Advanced without coaching and with coaching. very useful for preparing students. These 12th grade handwritten notes on electric charges and electric fields are made by top jee mains faculty members and are very helpful for cracking jee mains exams.